External Power Supplies (EPS) are devices used to supply electricity to, and to charge built-in batteries of electronic and electric devices such as laptops, mobile phones, tablets, MP3 players, electronic cigarettes, electric tooth brushes, electric shavers, etc. For products without built-in batteries, they serve as the main continuous source of power – for example standalone loudspeakers or computer network equipment such as modems and routers. EPSs are not the same as battery chargers, which charge stand-alone batteries or battery packs and which are exempted from this ecodesign regulation.
An EPS transforms the 230 V mains voltage supplied by an electric socket to a lower voltage level suitable to the primary load product – often between 5 V and 20 V. It also often rectifies the Alternating Current (AC) from the electric socket to Direct Current (DC) typically used for household and office electric and electronic products. An EPS is contained in a physical enclosure separate from the device that constitutes the primary load, and it is connected to that device via a removable or hard-wired electrical connection, cable, cord or other wiring.
Only EPS with nameplate output power not exceeding 250 W are in the scope of the ecodesign regulation.
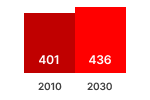
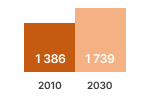
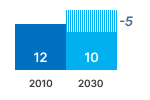
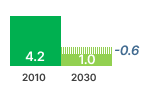
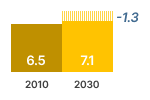
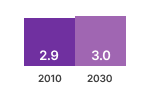
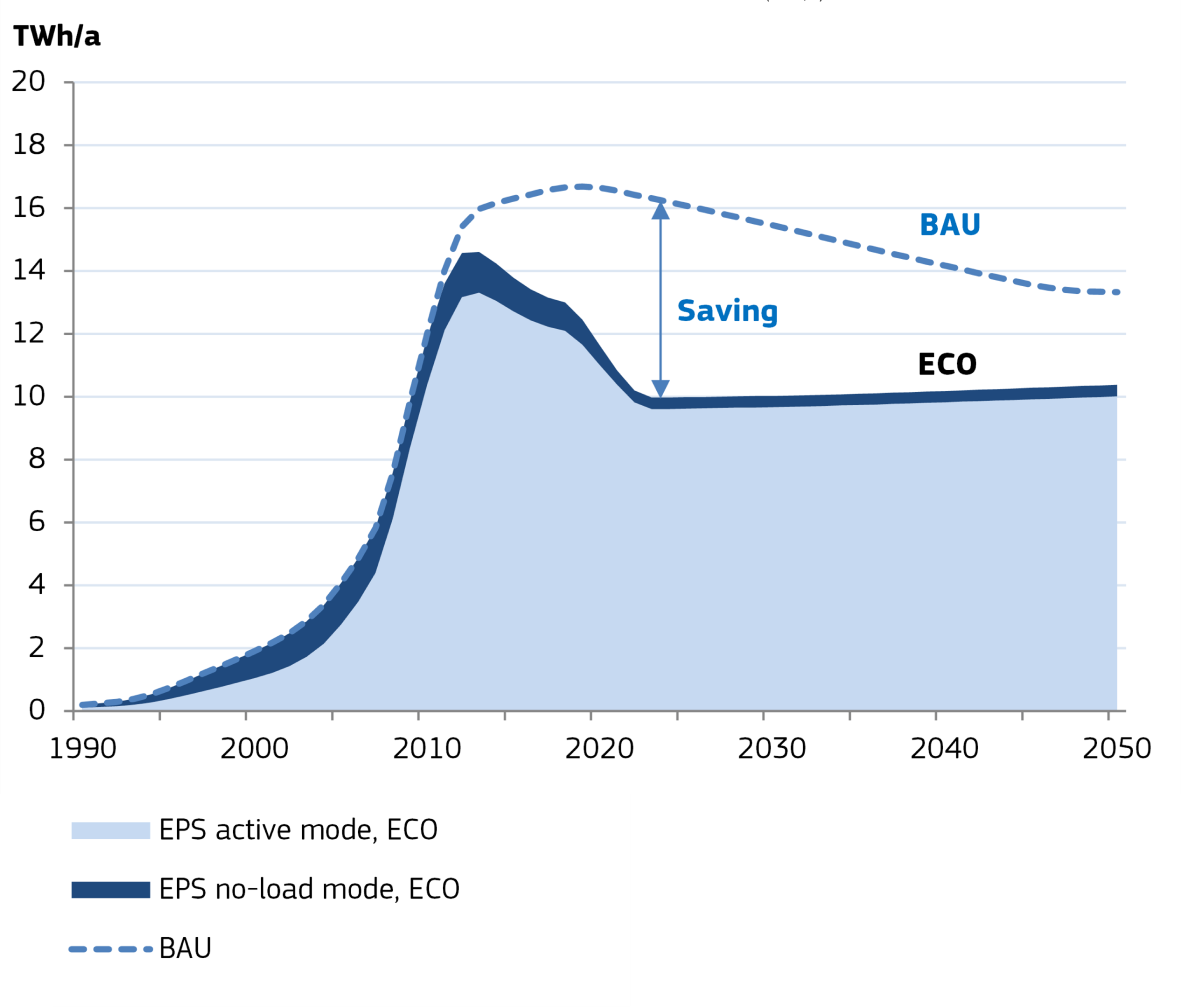
Source: estimations from the Ecodesign Impact Accounting Overview Report 2023