Ecodesign regulation 66/2014 covers domestic ovens, hobs (gas and electric) and range hoods (electric). There are no Energy Labelling requirements for hobs. Hobs are also subject to the Standby regulation 2023/826.
Scope
The following table shows some examples of products in scope and out of scope in the Ecodesign Regulation:
| In Scope | Out of Scope |
|---|---|
|
|
Check the complete list in the Ecodesign Regulation and Energy Labelling Regulation.
Ecodesign Requirements
Ecodesign regulations apply to all hobs sold in the EU. These regulations set requirements for:
- energy efficiency
- performance
- product information
Highlights
In 2020, 233 million hobs were installed in EU27 of which 66% electric and 34% gas. In the 2020 – 2030 period, sales of electric hobs are expected to increase by 21% from 11.5 to 12.8 million, while those of gas hobs are decreasing by 10%, from 5 to 4.5 mln. The result is an increase in the hobs stock to 250 mln in 2030 (+8%), and an increase in the electric share (71% of installed hobs in 2030).
Facts & Figures
This graphic shows the estimated sales, stock, energy consumption (primary, electric or fuel), greenhouse gas emissions, consumer expenses and business revenues for years 2010 and 2030. The estimated values inside the graph bars include the effects of Ecodesign and Energy Labelling measures.
The difference with the business as usual (BAU) scenario without these estimated measures is shown next to the graph bar. These estimated figures indicate the estimated savings obtained due to the estimated measures.
Product: Cooking Appliances Measures: Regulation (EU) 66/2014, Regulation (EU) 65/2014 |
|---|
| The striped lines in the charts show the 'Effect of the Regulations' |
SALES (x1000 units) 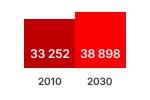 | STOCK (x1000 units) 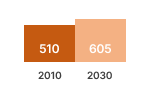 | Primary Energy 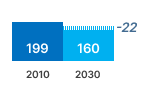 |
GHG-EMISSION 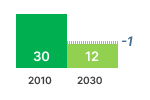 | CONSUMER EXPENSES 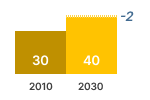 | REVENUES 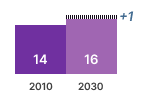 |
Source: estimations from the Ecodesign Impact Accounting Overview Report 2024
In 2020, 233 million hobs were in use in the EU27, slightly over 1 hob per household. The share of electric hobs is growing, from 43% in 1990, to 66% in 2020, and expected 71% in 2030. The share of gas hobs is decreasing. Cooking on oil, wood or coal is not in scope of the Ecodesign and Labelling regulations and thus not counted here.
The heat produced by all electric and gas hobs operating in the EU27 in 2020 is equivalent to heating 286 billion litres of water by 75°C and keeping it warm for 20 minutes.
Due to Ecodesign regulation, the efficiency of gas hobs has improved by 2% compared to a situation without measures. The average efficiency of new sold gas hobs in 2020 was 62.4%, corresponding to an average annual consumption of 290 kWh of gas (≈ 27 cubic meters).
Due to Ecodesign regulations, the efficiency of electric hobs in 2020 has improved by 4% compared to a situation without measures. This is mainly due to reducing the standby powers from 1.4 W to 0.5 W. The average electric efficiency of new sold electric hobs in 2020 was 78.3%, corresponding to an average annual consumption of 231 kWh of electricity.
Considering 48% efficiency during electricity generation (PEF 2.1), the primary energy efficiency of electric hobs is around 37%, and thus lower than for gas hobs.
The regulations saved 2.3 TWh of primary energy in 2020, projected to increase to 3.4 TWh by 2030 (of which 2.7 TWh due to standby). This is a 3.3% saving due to Ecodesign measures.
These savings are 0.02% of the total EU27 primary energy consumption in 2020.
Due to Ecodesign measures, EU27 users will save € 0.1 billion (1%) on hobs in 2030. This means € 0.80 per household per year.
Expected Savings
The Ecodesign regulation sets gradually more severe energy efficiency requirements in 3 tiers, in 2015, 2016 and 2019. There is no energy labelling for hobs.
The total primary energy consumption by Cooking Appliances (gas consumed plus fuel needed to generate the consumed electricity at PEF 2.5) was 205 TWh/a in 2020, of which 9 TWh for electric hobs in low-power modes. Without measures, the energy consumption in 2030 is expected to be 182 TWh/a (at PEF 1.9). With measures this is expected to drop to 160 TWh/a (-22 TWh/a, -12%). The major part of these savings is due to low-power modes of electric hobs and ovens (52%), range hoods (27%) and on-mode of electric ovens (13%).
Due to the lower primary energy use, the 2030 GHG-emissions related to the use of cooking appliances decrease from 14 Mt CO2eq/a (without measures) to 12 Mt CO2eq/a.
Total EU27 Primary Energy Saving for Cooking Appliances
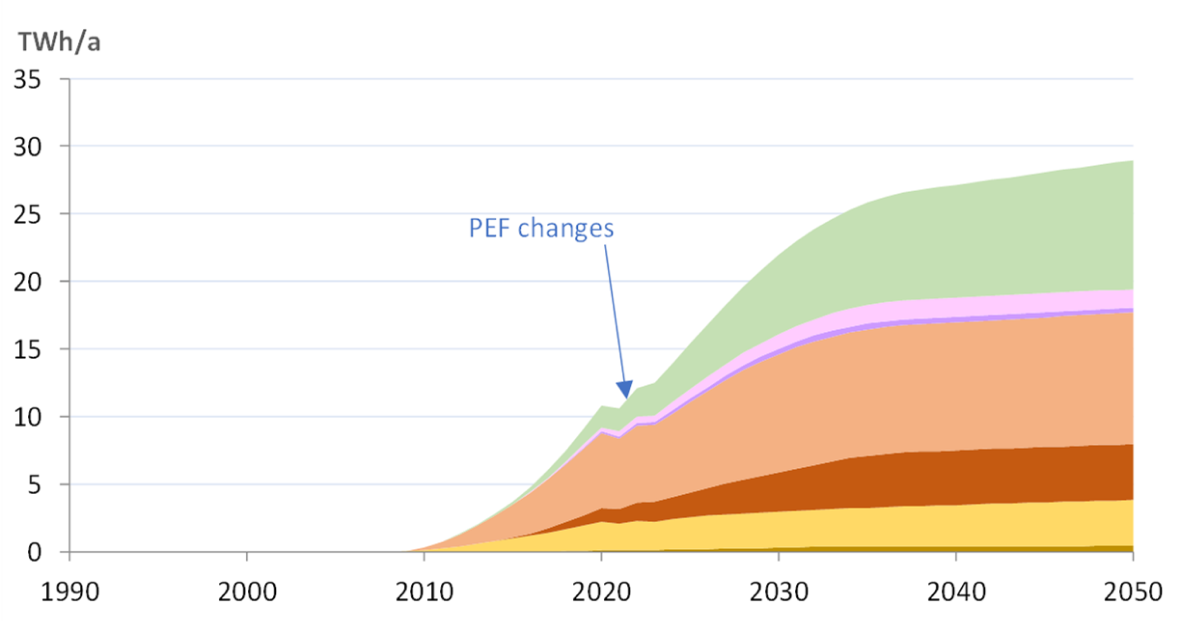

Source: estimations from the Ecodesign Impact Accounting Overview Report 2024

Policy
Ongoing legislative work
Please check the ongoing initiatives on the Have your say portal.
Commission Regulation (EU) 66/2014 of 14 January 2014 implementing Directive 2009/125/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council with regard to ecodesign requirements for domestic ovens, hobs and range hoods Text with EEA relevance. More info on Delegated Act.
Delegated Regulation (EU) 65/2014 of 1 October 2013 supplementing Directive 2010/30/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council with regard to the energy labelling of domestic ovens and range hoods Text with EEA relevance.
Disclaimer: please pay attention to possible updates/changes as indicated in the Official Journal (green dot)

