Refrigerating appliances with a direct sales function (formerly Commercial Refrigeration (CF)) are those used to display refrigerated or frozen foods or drinks. Typically they can be accessed directly by consumers in e.g. supermarkets, public indoor spaces and offices.
Many supermarket models are vertical cabinets with various shelves from which people take e.g. their milk, butter, cheese. Others are more like horizontal chests, e.g. for ice-cream, pizzas, meat. Refrigerated models can be open (direct access) or closed (typically by glass doors or lids); freezers are usually closed. EIA distinguishes 3 supermarket models: the ‘open chilled vertical multi deck’ (RVC2), the ‘open horizontal frozen island’ (RHF4) and ‘other supermarket display (non-BCs)’. For space, noise and efficiency reasons, supermarket models can have a remote configuration (R), meaning that the condensing unit (CU), which releases the heat extracted from the cabinets to the environment, is not integrated in the display but located elsewhere. The energy consumption of a remote CU is anyway counted as part of that of the CF appliance. CUs are also regulated (and reported in the EIA) as separate products, but double-counting of energy and savings is avoided when computing PF totals.
CF appliances used in public indoor spaces and offices are mostly ‘plug-in’ (with integrated CU). The user puts money in the appliance, chooses the desired snack or beverage, and then collects it from the drawer. EIA reports data for ‘beverage coolers’ and ‘spiral vending machines’. The last EIA product group in CF is ‘plug-in horizontal ice-cream freezers’.
Source: estimations from the Ecodesign Impact Accounting Overview Report 2024
Scope
The following table shows some examples of products in scope and out of scope in the Ecodesign Regulation:
| In Scope | Out of Scope |
|---|---|
|
|
Check the complete list in the Ecodesign Regulation and Energy Labelling Regulation.
Ecodesign Requirements
Rules on Ecodesign for refrigerating appliances with a direct sales function apply from 1 March 2021 under Regulation (EU) 2019/2024.
Energy Label
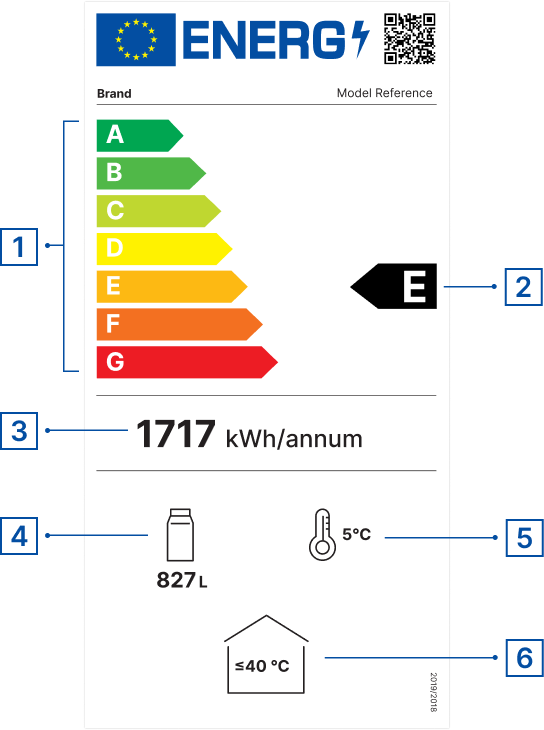
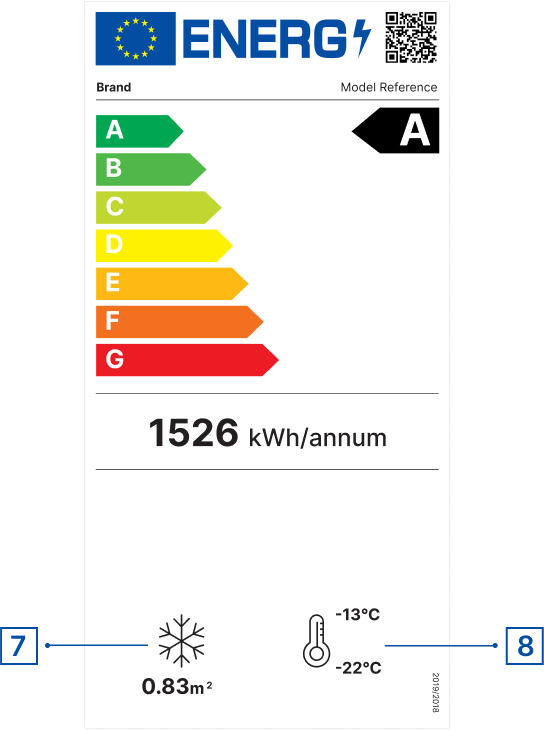
The EU energy labels for refrigerating appliances with a direct sales function use, as of 1 March 2021, a scale from A (most efficient) to G (least efficient) under Regulation (EU) 2019/2018. The labels provide information on the product’s
- energy efficiency class
- energy consumption
- volume or display areas of the compartments
- temperature of the compartments
For beverage coolers and ice-cream freezers, the labels also show the maximum ambient temperature.
The European Product Registry for Energy Labelling (EPREL) offers more detailed information on models placed on the EU market. This can be accessed by scanning the QR code featured on the new energy labels. The database provides additional information such as the consumption in standby mode, panel technology, whether voice recognition, automatic brightness control and a room sensor are present, or the minimum duration of guarantee offered by the supplier.
| Understanding the Commercial Refrigerator Energy Label | ||
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
|
Facts & Figures
This graphic shows the estimated sales, stock, energy consumption (primary, electric or fuel), greenhouse gas emissions, consumer expenses and business revenues for years 2010 and 2030. The estimated values inside the graph bars are those from the EIA ECO-scenario, they include the effects of Ecodesign and Energy Labelling measures.
The difference with the business as usual (BAU) scenario without these measures is shown next to the graph bar. These figures indicate the estimated savings obtained due to the measures.
Product: Refrigerating appliances with a direct sales function Measures: Regulation (EU) 2019/2024, Regulation (EU) 2019/2018 |
|---|
| The striped lines in the charts show the 'Effect of the Regulations' |
SALES (x1000 units) 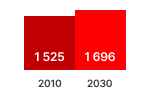 | STOCK (x1000 units) 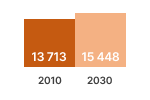 | Electricity (TWh/a) 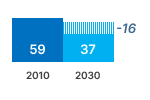 |
GHG-EMISSION  | CONSUMER EXPENSES 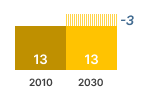 | REVENUES 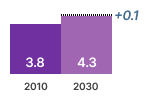 |
Source: estimations from the Ecodesign Impact Accounting Overview Report 2024
In 2020, 14.4 million refrigerating appliances with direct sales function (commercial fridges, CFs) were in use in the EU27. They cooled a net volume of 17.4 million m3, of which 20% was used for beverage coolers (@ 1-10°C), 3% for spiral vending machines (@ 1-7°C) and 5% for ice cream freezers (@-18/-15°C). The remaining 72% of the volume is used in supermarket display fridges (vertical chilled multi-decks, horizontal frozen islands, and other models).
In 1990, the average electricity consumption of sold commercial fridges was 6531 kWh/a. In 2030, without measures, this was expected to improve to 4161 kWh/a, but due to the regulations it is projected to reduce further to 2373 kWh/a (-43%).
The Ecodesign and Energy Labelling regulations for CFs are from 2019, so their effect in 2020 was negligible.
The regulations are forecasted to save 16 TWh of electricity in 2030, with an increase to 23 TWh by 2040. This is a 42% saving due to Ecodesign and Energy Labelling.
The projected 2040 savings are 0.96% of the total EU27 electricity consumption in 2020, and close to the annual electricity consumption of Slovakia.
Due to Ecodesign and Energy Labelling measures, EU27 users are forecasted to save € 3.4 billion on commercial fridges in 2030, projected to increase to € 4.8 billion in 2040. This means a 21% saving in 2030 and a 30% saving in 2040.
Expected Savings
ENERGY SAVINGS
In 2020, 14.4 million CF appliances were installed in EU27 and this number is expected to increase to 15.4 mln (+7%) by 2030. Around 45% are beverage coolers. A minority (30%) of the appliances is installed in super-markets.
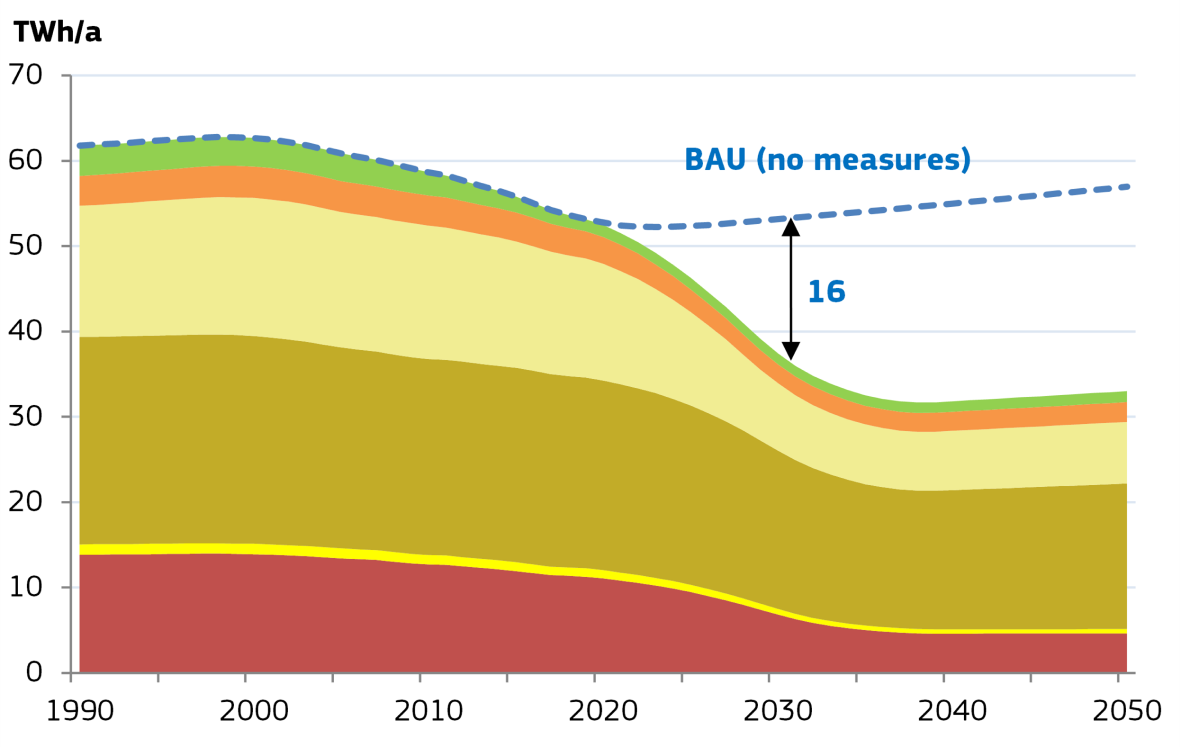
However, this minority is responsible for 65% of the electricity consumption. Total EU27 electricity use by CF was 52 TWh/a in 2020. Without measures this would remain at 53 TWh/a in 2030, notwithstanding the 8% stock increase. The introduction of Ecodesign and Labelling measures is projected to reduce this consumption in 2030 to 37 TWh/a (-16 TWh/ a or -30%).
In 2030 this corresponds to 3.4 billion euros savings on (commercial) expenditure in 2030, 0 due to lower electricity costs.
Total EU27 Electricity Consumption for Refrigeration with a Direct Sales Function
Source: estimations from the Ecodesign Impact Accounting Overview Report 2024

Suppliers
Suppliers shall ensure that:
(a) each refrigerating appliance is supplied with a printed label in the format as set out in Annex III;
(b) the parameters of the product information sheet, set out in Annex V, are entered into the product database;
(c) if specifically requested by the dealer, the product information sheet shall be made available in printed form;
(d) the content of the technical documentation, set out in Annex VI, is entered into the product database;
(e) any visual advertisement for a specific model of refrigerating appliances contains the energy efficiency class and the range of energy efficiency classes available on the label in accordance with Annex VII and Annex VIII;
(f) any technical promotional material concerning a specific model of refrigerating appliances, including technical pro motional material on the internet, which describes its specific technical parameters includes the energy efficiency class of that model and the range of energy efficiency classes available on the label, in accordance with Annex VII;
(g) an electronic label in the format and containing the information, as set out in Annex III, is made available to dealers for each refrigerating appliance model;
(h) an electronic product information sheet, as set out in Annex V, is made available to dealers for each refrigerating appliance model.

Dealers
Dealers shall ensure that:
(a) each refrigerating appliance, at the point of sale, including at trade fairs, bears the label provided by suppliers in accordance with point 1(a) of Article 3, with the label being displayed for built-in appliances in such a way as to be clearly visible, and for all other refrigerating appliances in such a way as to be clearly visible on the outside of the front or top of the refrigerating appliance;
(b) in the event of distance selling, the label and product information sheet are provided in accordance with Annexes VII and VIII;
(c) any visual advertisement for a specific model of refrigerating appliance, including on the internet, contains the energy efficiency class and the range of energy efficiency classes available on the label, in accordance with Annex VII;
(d) any technical promotional material concerning a specific model of refrigerating appliance, including technical pro motional material on the internet, which describes its specific technical parameters includes the energy efficiency class of that model and the range of energy efficiency classes available on the label, in accordance with Annex VII.

Policy
Ongoing legislative work
Please check the ongoing initiatives on the Have your say portal.
Regulation (EU) 2019/2024 of 1 October 2019 laying down Ecodesign requirements for refrigerating appliances with a direct sales function pursuant to Directive 2009/125/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council (OJ L 315, 5.12.2019, pp. 313-334)
Regulation (EU) 2019/2018 of 11 March 2019 supplementing Regulation (EU) 2017/1369 of the European Parliament and of the Council with regard to Energy Labelling of refrigerating appliances with a direct sales function (OJ L 315, 5.12.2019, pp. 155-186)
What is the aim of the regulations ?
- Regulation (EU) 2019/2024 establishes Ecodesign requirements for the placing on the market or putting into service mains-operated refrigerating appliances which have a direct sales function
- Delegated Regulation (EU) 2019/2018 lays down rules on the labelling of, and supply of additional product information on, the same refrigerating appliances.
Disclaimer: please pay attention to possible updates/changes as indicated in the Official Journal (green dot)
Useful Links
Regulation (EU) 2017/1369 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 4 July 2017 setting a framework for Energy Labelling and repealing Directive 2010/30/EU (OJ L 198, 28.7.2017, pp. 1-23)
Regulation (EU) 517/2014 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 April 2014 on fluorinated greenhouse gases and repealing Regulation (EC) 842/2006 Text with EEA relevance OJ L 150, 20.5.2014, p. 195-230
Directive 2012/19/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 4 July 2012 on waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) (OJ L 197, 24.7.2012, pp. 38-71)
Directive 2009/125/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 21 October 2009 establishing a framework for the setting of Ecodesign requirements for energy-related products (OJ L 285, 31.10.2009, pp. 10-35)
Regulation (EU) 2021/340 amending Regulations (EU) 2019/2013 to 2018
Regulation (EU) 2021/341 amending Regulations (EU) 2019/424, 1781 and 2020 to 2024

